Chemiluminescence immunoassays (ChLIA) from EUROIMMUN use magnetic particles coated with antibodies or antigens as a solid phase to detect specific antigens or antibodies in patient samples by means of chemiluminescence signals.
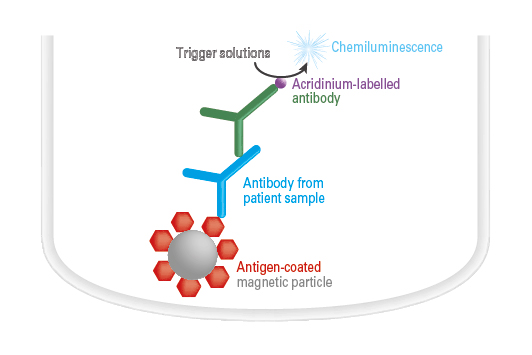 Antibody detection by ChLIA
Antibody detection by ChLIA
The antigen-coated magnetic particles are incubated with diluted samples. If a sample contains specific antibodies directed against the antigen, these bind to the antigen-coated magnetic particles. In the next step, acridinium-labelled antibody (conjugate) is added. This binds to the specific antibodies. A trigger solution is then added to induce a chemiluminescence reaction. The resulting light signal is proportional to the antibody concentration in the sample within the measurement range and is automatically converted into a concentration by the instrument.
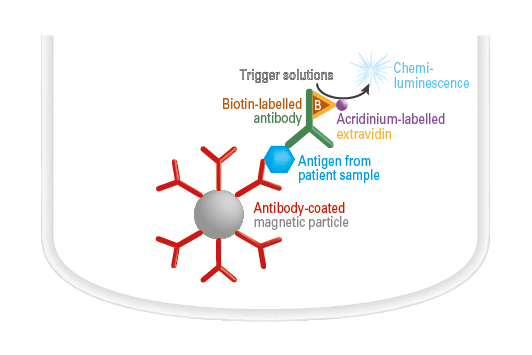 Antigen detection by ChLIA
Antigen detection by ChLIA
The antibody-coated magnetic particles are incubated with the sample and an antigen-specific biotinylated antibody. During the incubation, the antigen is bound by the magnetic particle-coupled antibody as well as by the biotinylated antibody. In the next step, acridinium-labelled ExtrAvidin (conjugate) is added. This binds to the biotinylated antibody. A trigger solution is then added to induce a chemiluminescence reaction. The resulting light signal is proportional to the antigen concentration in the sample within the indicated measurement range and is converted automatically into a concentration by the instrument.
