RIA (precipitation technique)
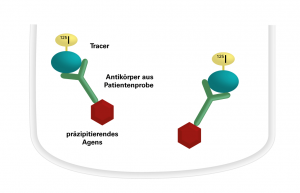 The patient sera to be investigated are incubated with I-125-labelled antigen in polystyrene tubes. The specific antibodies in the sera bind to the antigen. In a second incubation step, the resulting antigen-antibody complexes are precipitated by adding a precipitation agent. After washing of the precipitate with buffer, centrifugation and decanting of the liquid supernatant, the radioactivity of the precipitate is measured with a gamma counter. The intensity of the radioactive radiation is proportional to the concentration of the specific antibodies in the patient serum. The quantitative evaluation is performed based on a calibration curve.
The patient sera to be investigated are incubated with I-125-labelled antigen in polystyrene tubes. The specific antibodies in the sera bind to the antigen. In a second incubation step, the resulting antigen-antibody complexes are precipitated by adding a precipitation agent. After washing of the precipitate with buffer, centrifugation and decanting of the liquid supernatant, the radioactivity of the precipitate is measured with a gamma counter. The intensity of the radioactive radiation is proportional to the concentration of the specific antibodies in the patient serum. The quantitative evaluation is performed based on a calibration curve.
RIA/IRMA (coated tubes)
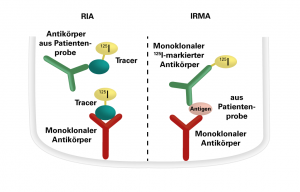 RIA: The RIAs with coated tubes are competitive ligand assays for detection of antibodies and antigens. The intensity of the radioactive radiation is inversely proportional to the concentration of the specific antibodies or the antigen in the patient sample. The quantitative evaluation of the antigen/antibody concentration is performed based on a calibration curve.
RIA: The RIAs with coated tubes are competitive ligand assays for detection of antibodies and antigens. The intensity of the radioactive radiation is inversely proportional to the concentration of the specific antibodies or the antigen in the patient sample. The quantitative evaluation of the antigen/antibody concentration is performed based on a calibration curve.
IRMA (immunoradiometric assays): The test principle is based on monoclonal antibodies bound directly or indirectly to the inner wall of the polystyrene tubes. The patient samples to be investigated are incubated together with monoclonal I-125-labelled antibodies in the coated tubes. The antigen in the patient samples is bound both by the immobilized antibodies and the I-125-labelled antibodies. A solid-phase bound sandwich complex is formed. The unbound I-125-labelled antibodies are removed by washing and subsequent decanting. The intensity of the radioactive radiation is proportional to the concentration of the antigens in the patient serum. The quantitative evaluation of the antigen concentration is performed based on a calibration curve.
Magnetic separation
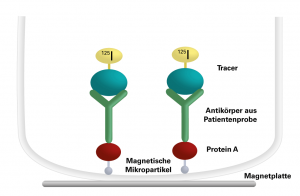 In the first analysis step, the samples to be investigated are incubated with the I-125-labelled tracer, so that specific antibodies from the patient sample bind to the tracer. The tracer-antibody complex is precipitated by incubating it with protein A suspension in a second step. Protein A is coupled to magnetic microparticles and binds to the antibodies. After placing the tubes onto a magnetic plate, the unbound I-125 labelled tracer can be decanted. The remaining radioactivity is measured with a gamma counter and is proportional to the concentration of the specific antibody in the patient sample.
In the first analysis step, the samples to be investigated are incubated with the I-125-labelled tracer, so that specific antibodies from the patient sample bind to the tracer. The tracer-antibody complex is precipitated by incubating it with protein A suspension in a second step. Protein A is coupled to magnetic microparticles and binds to the antibodies. After placing the tubes onto a magnetic plate, the unbound I-125 labelled tracer can be decanted. The remaining radioactivity is measured with a gamma counter and is proportional to the concentration of the specific antibody in the patient sample.